A Pageable and Sortable WPF DataGrid
Introduction
There was recently a need for a WPF DataGrid paging and sorting functionality in a project I am currently working on. The goal was to find a reusable solution that can easily be used across the project. A complete working sample can be found on Github. In this blog post, we will go through the main points of the implementation.
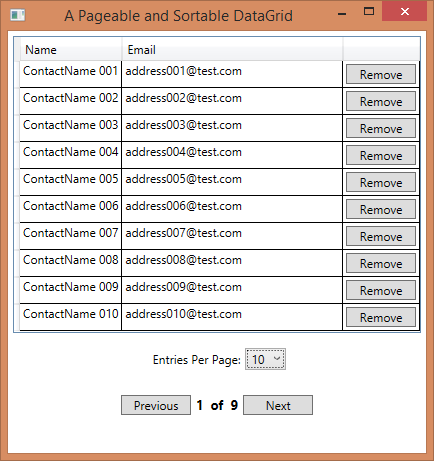
This DataGrid has the following features:
- Page navigation
- Dynamically adjustable page size
- Sorting functionality for the whole item collection
- Item addition at the top of the first page
- Item removal while remaining on the selected page
Implementation
The solution can be divided into two parts. We will start with Paging and continue with Sorting. Paging was solely implemented in the ViewModel. Sorting required the ViewModel to be extended and the DataGrid (class) to be subclassed.
Although we could have encapsulated the ViewModel paging and sorting functionality in one class, we are going to use two classes, one for paging and another one (which inherits from the paging class) for the sorting so that the implementation is a bit more clear.
Paging
As said earlier, we are going to implement the functionality using only the ViewModel. We will create a new PageableCollection<T> class which implements INotifyPropertyChanged, encapsulates all the paging logic and exposes an ObservableCollection<T> property, CurrentPageItems for the DataGrid’s ItemsSource to bind to.
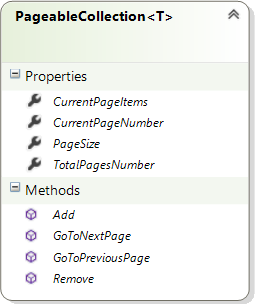
You can see the most important properties and methods in the above table. Although the names are self explanatory, here is a brief description for each one:
CurrentPageNumber: The number of the page we are currently on.
CurrentPageItems: An ObservableCollection<T> which contains the objects of type T that are listed on the current page. The ItemsSource of the DataGrid will be bound to this property
PageSize: The number of entries shown per page. Every time this property gets updated, the whole collection gets reset and returns to the first page.
TotalPagesNumber: The total number of pages, depending on the page size.
GoToNextPage, GoToPreviousPage: The two navigation void methods we will use to move to the next and previous page respectively.
Add: This method is used for adding a new item to our collection . The collection is reset with new item being inserted at the top of the first page.
Remove: This method is used for removing an item. The item gets removed while remaining on the same page.
If you only need the sorting functionality, you can directly use the PageableCollection<T> class below.
Sorting
The problem that has to be tackled is the fact that the DataGrid can only sort its ItemsSource. In our case, this only includes the items of the current page. Therefore, sorting has to be delegated from the DataGrid to the complete items list.
In order to achieve that, we have to use some code-behind and since we would like to develop a reusable component, we are going to encapsulate this functionality in a new class deriving from the DataGrid class.
The new SortableDataGrid class will be having an ISortable dependency property
and the Sort method is going to be called every time the sorting event fires in the Grid. Let us have a look at the class:
The new SortableDataGrid class:
- Has an
ISortabledependency propertyFullItemsSource - Overrides the
OnInitializedevent handler and stores the initial column which is used for sorting. - Overrides the
OnSortingevent handler, cancels the default sorting functionality and calls the Sort method of theISortabledependency property with the property name and the sorting direction as input parameters. - Overrides the
OnItemsSourceChangedevent handler in order to retain the sorting direction during page navigation.
The ISortable interface gets implemented by the SortablePageableCollection where the property to be used for sorting is found using reflection:
Finally, in our XAML code, all we have to do is set the bindings for both the FullItemsSource and ItemsSource.